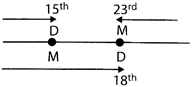
 more...
more...  (a) 64 (b) 100
(c) 81 (d) 144
Explanation: (d)
Figure 1 : \[{{\left[ \left( 8\text{ }+\text{ }4 \right)\text{ }-\text{ }\left( 6\text{ }+\text{ }3 \right) \right]}^{2}}=9\]
Figure 2 : \[{{\left[ \left( 7\text{ }+\text{ }9 \right)\text{ }-\text{ }\left( 5\text{ }+\text{ }4 \right) \right]}^{2}}=49\]
Figure 3 : \[{{\left[ \left( 8\text{ }+\text{ }9 \right)\text{ }-\text{ }\left( 2\text{ }+\text{ }3 \right) \right]}^{2}}=\text{ }144\]
Thus, the required number is 144.
2. Select a letter from the options which will replace the'?'.
(a) 64 (b) 100
(c) 81 (d) 144
Explanation: (d)
Figure 1 : \[{{\left[ \left( 8\text{ }+\text{ }4 \right)\text{ }-\text{ }\left( 6\text{ }+\text{ }3 \right) \right]}^{2}}=9\]
Figure 2 : \[{{\left[ \left( 7\text{ }+\text{ }9 \right)\text{ }-\text{ }\left( 5\text{ }+\text{ }4 \right) \right]}^{2}}=49\]
Figure 3 : \[{{\left[ \left( 8\text{ }+\text{ }9 \right)\text{ }-\text{ }\left( 2\text{ }+\text{ }3 \right) \right]}^{2}}=\text{ }144\]
Thus, the required number is 144.
2. Select a letter from the options which will replace the'?'.
 (a) I (b) J
(c) K (d) L
Explanation: (b)
Let us consider row-wise,
Row 1: \[A+2=C;\text{ }C+2=E;\]
Row 3: \[K+2=M\text{ };\text{ }M+2=0\]
Row 2: \[F+2=H\] So, \[H+2=\{\,J\,\}\]
Thus, the required letter is ?J?.
3. Find the missing number in the given figure.
(a) I (b) J
(c) K (d) L
Explanation: (b)
Let us consider row-wise,
Row 1: \[A+2=C;\text{ }C+2=E;\]
Row 3: \[K+2=M\text{ };\text{ }M+2=0\]
Row 2: \[F+2=H\] So, \[H+2=\{\,J\,\}\]
Thus, the required letter is ?J?.
3. Find the missing number in the given figure.
 (a) 5 (b) 9
(c) 11 (d) 13
Explanation: (b)
Observing the given design, we see that
Place value of W=23 and place value of T=20
Here, 23 - 20 = 3
The same rule is followed by the other two sets.
Thus, place value of P = 16
Place value of G = 7
So, required number =16-7=9.
(a) 5 (b) 9
(c) 11 (d) 13
Explanation: (b)
Observing the given design, we see that
Place value of W=23 and place value of T=20
Here, 23 - 20 = 3
The same rule is followed by the other two sets.
Thus, place value of P = 16
Place value of G = 7
So, required number =16-7=9.
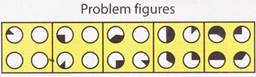 (a)
(a)  (b)
(b)  (c)
(c)  (d)
(d)  Explanation (a):
Area enclosed by black shaded region in top left circle, increases by \[45{}^\circ \] and rotates anticlockwise by \[45{}^\circ \] in each stage.
The same procedure happens for other circles.
So the correct option is (a).
2. Choose the missing figure from the four options to substitute the question mark(?), so that a series is formed.
Explanation (a):
Area enclosed by black shaded region in top left circle, increases by \[45{}^\circ \] and rotates anticlockwise by \[45{}^\circ \] in each stage.
The same procedure happens for other circles.
So the correct option is (a).
2. Choose the missing figure from the four options to substitute the question mark(?), so that a series is formed.
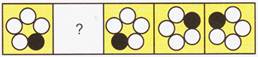 (a)
(a)  (b)
(b)  (c)
(c)  (d)
(d)  Explanation (c):
We observe that the black shade in a circle moves 2 steps anticlockwise in each step.
So, the correct option is (c).
Explanation (c):
We observe that the black shade in a circle moves 2 steps anticlockwise in each step.
So, the correct option is (c).
 (a)
(a)  (b)
(b)  (c)
(c)  (d)
(d)  Explanation (a):
First figure of the pair converted into three similar figures but reduced in size.
These three figures from left to right are shaded, contains slanting lines and unshaded respectively.
All these features are followed by figure in option (a).
2. Choose odd one out.
(a)
Explanation (a):
First figure of the pair converted into three similar figures but reduced in size.
These three figures from left to right are shaded, contains slanting lines and unshaded respectively.
All these features are followed by figure in option (a).
2. Choose odd one out.
(a)  (b)
(b)  more...
more... 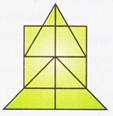 (a) 14 (b) 15
(c) 16 (d) 17
Explanation (c):
Let us label the given figure as shown in the adjoining figure.
(a) 14 (b) 15
(c) 16 (d) 17
Explanation (c):
Let us label the given figure as shown in the adjoining figure.
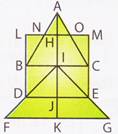 Triangles made up of one segment: ANH, AOH, LBN, MCO, BDI, CEI, IDJ, IEJ.
These are 8 triangles.
Triangles made up of two segments: ABI, ACI, IFK, IGK, ANO, IDE.
These are 6 triangles.
No triangles made up of 3 segments.
Triangles made up of 4 segments: ABC, IFG.
These are 2 triangles.
Total number of triangles
Triangles made up of one segment: ANH, AOH, LBN, MCO, BDI, CEI, IDJ, IEJ.
These are 8 triangles.
Triangles made up of two segments: ABI, ACI, IFK, IGK, ANO, IDE.
These are 6 triangles.
No triangles made up of 3 segments.
Triangles made up of 4 segments: ABC, IFG.
These are 2 triangles.
Total number of triangles 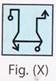 (a)
(a) 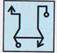 (b)
(b) 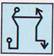 (c)
(c) 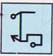 (d)
(d)  Explanation (a):
Explanation (a):
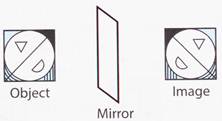
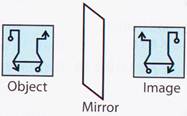 2. Choose the correct mirror image of the following combination.
T 3 S 4 P 5 H 6
(a) 6 H S 4 P 4 S 3 T (b) H 6 P 5 S 4 T 3
(c)
2. Choose the correct mirror image of the following combination.
T 3 S 4 P 5 H 6
(a) 6 H S 4 P 4 S 3 T (b) H 6 P 5 S 4 T 3
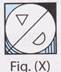
(c) 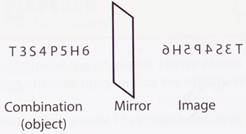 3. Select the correct mirror image of the Fig. (X).
3. Select the correct mirror image of the Fig. (X).
 (a)
(a)  (b)
(b)  (c)
(c) 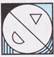 (d)
(d)  Explanation (c):
Explanation (c):
 4. Choose the correct water image of the given combination.
V A Y U 8 4 3 6
(a)
4. Choose the correct water image of the given combination.
V A Y U 8 4 3 6
(a)  (a)
(a)  (b)
(b)  (c)
(c)  (d)
(d)  Explanation (d):
Explanation (d):
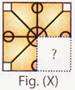
 2. Select a figure from the options which will complete the pattern in Fig. (X)?
2. Select a figure from the options which will complete the pattern in Fig. (X)?
 (a)
(a) 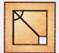 (b)
(b) 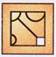 (c)
(c) 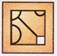 (d)
(d) 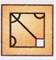 Explanation (d):
Explanation (d):
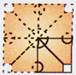
 (a)
(a)  (b)
(b) 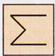 (c)
(c)  (d)
(d)  Explanation (c):
The rule is followed row-wise in each figure.
The alphabets are rotated
Explanation (c):
The rule is followed row-wise in each figure.
The alphabets are rotated 
 (a)
(a) 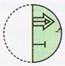 (b)
(b) 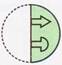 (c)
(c)  (d)
(d) 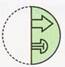 Explanation (c):
It is clear from the four options the left half of the transparent sheet has been placed over the right half.
The left arrow is smaller than the right one, so it lies in the interior of the right arrow.
For other two shapes, the right shape is smaller than the left one.
So it lies in the interior of the left shape.
Thus, option (c) is correct.
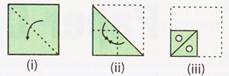
2. The three figures (i), (ii) and (iii) show a sequence of folding a sheet of paper.
Figure (iii) shows the manner in which the folded sheet has been cut out.
If then the sheet is unfolded which of the option figures (a), (b), (c), (d) would show the unfolded form?
Explanation (c):
It is clear from the four options the left half of the transparent sheet has been placed over the right half.
The left arrow is smaller than the right one, so it lies in the interior of the right arrow.
For other two shapes, the right shape is smaller than the left one.
So it lies in the interior of the left shape.
Thus, option (c) is correct.
2. The three figures (i), (ii) and (iii) show a sequence of folding a sheet of paper.
Figure (iii) shows the manner in which the folded sheet has been cut out.
If then the sheet is unfolded which of the option figures (a), (b), (c), (d) would show the unfolded form?
 (a)
(a)  (b)
(b) 
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
