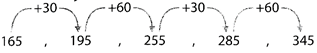
 Clearly, the required term = 345 + 30 = 375.
2. Choose the missing term.
43, ?, 66, 83, 91, 106, 123
(a) 58 (b) 51
(c) 60 (d) 56
Explanation (b):
We see that
83 - 66 = 17
91-83=8
106-91 = 15
123- 106= 17
So, the difference between four consecutive terms in pairs is 8, 15, 17; 8, 15, 17.
\[\therefore \]Required term = 43 + 8 = 51.
3. Identify the wrong number in the series.
69, 55, 26, 13, 5
(a) 55 (b) 5
(c) 26 (d) 13
Explanation (b):
Clearly, in the given series, each term is one more than the product of the digits of the preceding term.
Thus, \[\left( 6\times 9 \right)+1=55,\left( 5\times 5 \right)+1=26,\left( 2\times 6 \right)+1=13.\]
So, 5 is wrong number in the series and must be replaced by \[\left( 1\times 3 \right)\]+1 i.e., 4.
Hence, the answer is (b).
4. Choose the missing term.
AB, DEF, HUK, ?, STUVWX
(a) MNOPQ (b) LMNOP
(c) LMNO (d) QRSTU
Explanation (a):
First letter of each term except the first term is two more than the last letter of the previous term.
1st letter of required term = more...
Clearly, the required term = 345 + 30 = 375.
2. Choose the missing term.
43, ?, 66, 83, 91, 106, 123
(a) 58 (b) 51
(c) 60 (d) 56
Explanation (b):
We see that
83 - 66 = 17
91-83=8
106-91 = 15
123- 106= 17
So, the difference between four consecutive terms in pairs is 8, 15, 17; 8, 15, 17.
\[\therefore \]Required term = 43 + 8 = 51.
3. Identify the wrong number in the series.
69, 55, 26, 13, 5
(a) 55 (b) 5
(c) 26 (d) 13
Explanation (b):
Clearly, in the given series, each term is one more than the product of the digits of the preceding term.
Thus, \[\left( 6\times 9 \right)+1=55,\left( 5\times 5 \right)+1=26,\left( 2\times 6 \right)+1=13.\]
So, 5 is wrong number in the series and must be replaced by \[\left( 1\times 3 \right)\]+1 i.e., 4.
Hence, the answer is (b).
4. Choose the missing term.
AB, DEF, HUK, ?, STUVWX
(a) MNOPQ (b) LMNOP
(c) LMNO (d) QRSTU
Explanation (a):
First letter of each term except the first term is two more than the last letter of the previous term.
1st letter of required term = more...  Similarly, we find
Similarly, we find
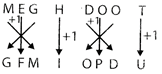 So, the correct option is (A).
4. If \[M\otimes N\] is to \[14\times 15,\] then \[P\otimes Q\] is to .......... .
(a) \[14\times 15\] (b) \[15\times 16\]
(c) \[17\times 18\] (d) \[16\times 17\]
Explanation: (c)
\[\otimes \] becomes the symbol 'x'. Letters become one more than numbers as their places in the English alphabet.
Therefore,
So, the correct option is (A).
4. If \[M\otimes N\] is to \[14\times 15,\] then \[P\otimes Q\] is to .......... .
(a) \[14\times 15\] (b) \[15\times 16\]
(c) \[17\times 18\] (d) \[16\times 17\]
Explanation: (c)
\[\otimes \] becomes the symbol 'x'. Letters become one more than numbers as their places in the English alphabet.
Therefore,
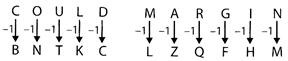 So, 'MOULDING' will be written as 'LNTKCHMF'.
2. In a code, CONTRIBUTE is written as ETUBIRTNOC. If POPULARISE is written in that code, then which letter will be in the 6th place when counted from the left end?
(a) P (b) L
(c) R (d) I
Explanation: (b)
In code language, the letters of the word are written in the reverse order.
So, POPULARISE will be written as \[E\text{ }S\text{ }I\text{ }R\text{ }AOU\,P\,O\,P.\]
Clearly, 6th letter is 'L
3. In a certain code, PRAISE is written as #@$27% and RESPIRE is written as @%7#2@%.
How is REPAIR written in that code?
(a) #2@%$@ (b) %@7#$2@
(c) @%#$2@ (d) @%$2#@
Explanation: (c)
From the given words and their codes, we conclude that
So, 'MOULDING' will be written as 'LNTKCHMF'.
2. In a code, CONTRIBUTE is written as ETUBIRTNOC. If POPULARISE is written in that code, then which letter will be in the 6th place when counted from the left end?
(a) P (b) L
(c) R (d) I
Explanation: (b)
In code language, the letters of the word are written in the reverse order.
So, POPULARISE will be written as \[E\text{ }S\text{ }I\text{ }R\text{ }AOU\,P\,O\,P.\]
Clearly, 6th letter is 'L
3. In a certain code, PRAISE is written as #@$27% and RESPIRE is written as @%7#2@%.
How is REPAIR written in that code?
(a) #2@%$@ (b) %@7#$2@
(c) @%#$2@ (d) @%$2#@
Explanation: (c)
From the given words and their codes, we conclude that
| Letter | Code | |||||||||||
| P | more...
In this section/ problems are based on blood relations. The process of solving these problems (puzzles) depends upon the deep knowledge of blood relations. The common relations are: Father, Mother, Grandparents/ Wife, Husband/Son, Daughter, Grandchild, Sister, Brother etc.
Remarks:
1. Relatives on the mother's side are called 'maternal'. For example, mother's brother is called maternal uncle.
2. Relatives on the father's side are called 'paternal'. For example, father's brother is called paternal uncle.
3. Assume a relation as paternal relation, unless stated otherwise.
EXAMPLE
1. A woman going with a boy is asked by another woman about the relationship between them.
The woman replied, "My maternal uncle and the uncle of his maternal uncle is the same."
How is the lady related with that boy?
(a) Grandmother and Grandson
(b) Mother and Son
(c) Aunt and Nephew
(d) Sister and brother
Explanations: (c)
The brother of woman's mother is the same as brother of the father of boy's maternal uncle. Also, the woman's mother's brother is the boy's maternal uncle's father, Thus, the woman's mother's brother's son is boy's maternal uncle, i.e., woman's mother's brother's daughter is boy's mother.
So, the woman and boy's mother are cousins. Thus, the woman is boy's aunt. Hence, the answer is (c).
2. A and B are brothers. C and D are sisters. A's son is D's brother. How is B related to C?
(a) Father (b) Brother
(c) Uncle (d) Grandfather
Explanation: (c)
Clearly, A's son is C's brother. This means C is the daughter of A. So, B is the uncle of C. Hence, the answer is (c).
3. If 'P + Q' means 'P is the father of Q',
In puzzle test, some information is provided in the form of a puzzle and hence one or more questions are put up on the basis of it.
To answer these questions, a student is required to simplify the puzzle in his/her own language.
The puzzle may be of any field such as:
1. Seating/placing arrangement.
2. Comparison of heights, weights, sizes, etc.
3. Family basis.
4. Sequential order of things.
EXAMPLE
1. Among four friends, Mohit is thrice the age of Kartik. Tarun is half times younger to Kartik.
Anuj is six years older to Kartik, but six years younger to Mohit. Who is the eldest?
(a) Tarun (b) Kartik
(c) Anuj (d) Mohit
Explanation: (d)
Mohit = 3 (Kartik)
Tarun =
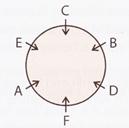 All face towards the centre
We observe that E is sitting between A and C.
All face towards the centre
We observe that E is sitting between A and C.
When an input of some numbers is given to a number generating machine, it gives sets of numbers in a specific pattern as an output.
Infect an input may be of letters/words or numbers or combination of both.
A student is required to analyses the data (input and output) and identify the pattern to answer the questions.
Let us write some commonly used patterns:
1. Arrangement of the given numbers in ascending/descending order.
2. Arrangement of the given numbers stepwise in the order: greatest, smallest, second greatest, second smallest, and so on.
3. Arrangement of given words in alphabetical and reverse alphabetical order.
4. Arrangement of a particular set of words in the reverse order, stepwise.
EXAMPLE
1. Direction (I-II): Study the following information to answer the questions given below:
A number arrangement machine when given an input of numbers, rearranges them by following a particular rule in each step. The following is an illustration of an input and steps of rearrangement.
|