Use of Different Conjunctions
(A) And, As well as
These two conjunctions are used to add one statements to another:

- The man is poor. The man is blind.
- The man is poor and blind.
- Robinson likes tea. Robinson likes coffee.
- Robinson likes tea as well as coffee.
- Anima and Twinkle are dancing.
- You as well he have lifted the box.
- Please come and sit beside me.
- Garry sells fruits and vegetables.
(B) Or, Either -- or, Neither --- nor -
These conjunctions are used to indicate a choice between one statement and another.

- Is he happy? Is he sad?
- Is he happy or sad?
- I will come. I will send Sanjeev.
- Either I will come or send Sanjeev.
- James is not my friend. He is not my brother.
- James is neither my friend nor my brother.
(C) But, still, yet
These conjunctions are used to express contrast between two statements.

- He is intelligent. He does not read.
- He is intelligent but he does not read.
- The teacher was angry. He did not scold the boy.
- The teacher was angry still he did not scold the boy.
- These books are costly. People buy them.
- These books are costly yet people buy them.
(D) So, therefore
These conjunctions are used to join two statements where one statement is proved by the other statement.

- He did not take umbrella. He got wet.
He did not take umbrella so he got wet.
- The boy stole bread from the shop. He was arrested by the police.
The boy stole bread from the shop, therefore he was arrested by the police.
(E) When, while
These conjunctions are used to join two statements to highlight the time of anaction.

- The cat is away. The mice play.
When the cats is away the mice play.
- I met Priya. I was in London.
I met Priya while I was in London.
(F) lf, Unless
These conjunctions are used to join two statements when a condition is shown.

- You give me money. I will return your pen.
If you give me money, I will return your pen.
- You make haste. You cannot reach home in time.
Unless you make haste you cannot reach home in time.
(G) As, Than
These
more...
 Fill in the blanks with suitable Conjunction.
Fill in the blanks with suitable Conjunction.
 Fill in the blanks with suitable Prepositions
Fill in the blanks with suitable Prepositions
 more...
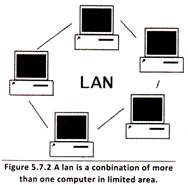
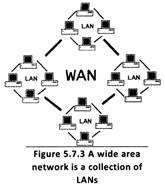
more... 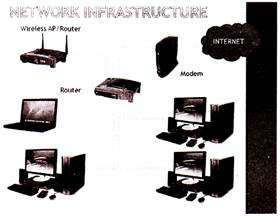 There are different types of networking methods available today but in this chapter you will read only two of them i.e. LAN and WAN.
There are different types of networking methods available today but in this chapter you will read only two of them i.e. LAN and WAN.

