 Polar region receives less Sun rays in comparison to equator and from the other parts of the earth. Hence the climate of the polar region is cold. The area at equator receives more...
Polar region receives less Sun rays in comparison to equator and from the other parts of the earth. Hence the climate of the polar region is cold. The area at equator receives more...
 A fuse consists of a strip of low melting alloy. In case of over loading or short circuiting, the alloy wire more...
A fuse consists of a strip of low melting alloy. In case of over loading or short circuiting, the alloy wire more...
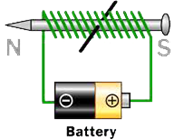
 A simple electric circuit is composed of a battery, wire, and a switch. One end of the wire is connected to the negative terminal of the battery and the other end of the wire is connected to the positive terminal of the battery. Switch is fitted in the wire in such a way that when switch is on, the wires of the circuit are connected and current is passed. When the switch is off, the more...
A simple electric circuit is composed of a battery, wire, and a switch. One end of the wire is connected to the negative terminal of the battery and the other end of the wire is connected to the positive terminal of the battery. Switch is fitted in the wire in such a way that when switch is on, the wires of the circuit are connected and current is passed. When the switch is off, the more...
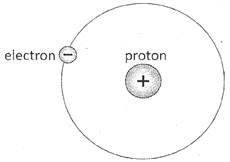 In an atom, number of protons is equal to the number of electrons. Therefore, atoms are neutral. But transfer of electrons from one atom to other atom causes the atoms to be charged. The atom, which looses the electrons gets positively charged because number of positively charged particle (protons) in the atom gets greater than that of negatively charged particles (electrons). Therefore, magnitude of total positive charge more...
In an atom, number of protons is equal to the number of electrons. Therefore, atoms are neutral. But transfer of electrons from one atom to other atom causes the atoms to be charged. The atom, which looses the electrons gets positively charged because number of positively charged particle (protons) in the atom gets greater than that of negatively charged particles (electrons). Therefore, magnitude of total positive charge more...
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
