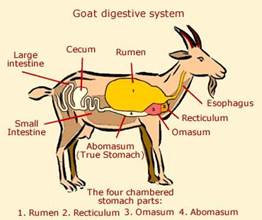
 These animals graze and take food through the mouth. In mouth food is mixed with saliva , secreted by the salivary glands. Teeth more...
These animals graze and take food through the mouth. In mouth food is mixed with saliva , secreted by the salivary glands. Teeth more...
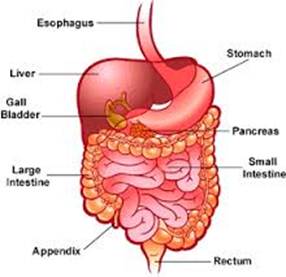
| Shape | Total no. of sides | Perimeter |
| more...
Learning Objectives:
Learning Objectives:
Learning Objectives:
Learning Objectives:
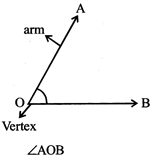 OA & OB are arms O is more...
OA & OB are arms O is more...
Articles CategoriesArchive
Trending Articles
You need to login to perform this action. |