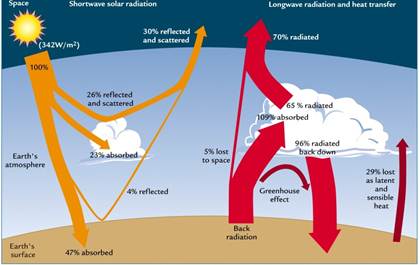
 Solar Radiation
In the figure below, a bundle of wood stick burns and radiates heat energy.
Solar Radiation
In the figure below, a bundle of wood stick burns and radiates heat energy.
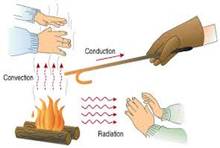 Radiation
Air around more...
Radiation
Air around more...
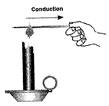
 An iron rod is heated Copper wire
An iron rod is heated Copper wire

 Steel Aluminum
Steel Aluminum
 Knife
more...
Knife
more...
 In the above picture an iron rod has been heated and heat is transferred from its rounded part to whole part. The rate of transfer of heat depends on the length of the rod and the amount of heat received by the rod from heat producing elements. The other parts of the rod gets heated by conduction. And the rods more...
In the above picture an iron rod has been heated and heat is transferred from its rounded part to whole part. The rate of transfer of heat depends on the length of the rod and the amount of heat received by the rod from heat producing elements. The other parts of the rod gets heated by conduction. And the rods more...

 more...
more...


You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
