-
question_answer1)
If in nature there may not be an element for which the principal quantum number n > 4, then the total possible number of elements will be [IIT 1983; MP PET 1999; RPMT 1999; RPET 2001]
A)
60 done
clear
B)
32 done
clear
C)
4 done
clear
D)
64 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer2)
In the Bohr's hydrogen atom model, the radius of the stationary orbit is directly proportional to (n = principle quantum number) [MNR 1988; SCRA 1994; CBSE PMT 1996; AIIMS 1999; DCE 2002]
A)
\[\beta \] done
clear
B)
n done
clear
C)
\[{{n}^{-2}}\] done
clear
D)
\[{{n}^{2}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer3)
In the nth orbit, the energy of an electron \[{{E}_{n}}=-\frac{13.6}{{{n}^{2}}}eV\]for hydrogen atom. The energy required to take the electron from first orbit to second orbit will be [MP PMT 1987; CPMT 1991, 97; RPMT 1999; DCE 2001; Kerala PMT 2004]
A)
\[10.2\ eV\] done
clear
B)
\[12.1\ eV\] done
clear
C)
\[13.6\ eV\] done
clear
D)
\[3.4\ eV\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer4)
In the following atoms and moleculates for the transition from n= 2 to n = 1, the spectral line of minimum wavelength will be produced by [IIT 1983]
A)
Hydrogen atom done
clear
B)
Deuterium atom done
clear
C)
Uni-ionized helium done
clear
D)
di-ionized lithium done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer5)
The Lyman series of hydrogen spectrum lies in the region [MNR 1993; MP PMT 1995; UPSEAT 2002]
A)
Infrared done
clear
B)
Visible done
clear
C)
Ultraviolet done
clear
D)
Of \[X-\] rays done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer6)
The size of an atom is of the order of [CPMT 1990; MP PMT 1984; KCET 1994]
A)
\[{{10}^{-8}}m\] done
clear
B)
\[{{10}^{-10}}m\] done
clear
C)
\[{{10}^{-12}}m\] done
clear
D)
\[{{10}^{-14}}m\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer7)
Which one of the series of hydrogen spectrum is in the visible region [RPMT 1999;MP PET 1990; MP PMT 1994; AFMC 1998; CBSE PMT 1990; MH CET 2004]
A)
Lyman series done
clear
B)
Balmer series done
clear
C)
Paschen series done
clear
D)
Bracket series done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer8)
The energy levels of the hydrogen spectrum is shown in figure. There are some transitions A, B, C, D and E. Transition A, B and C respectively represent [CPMT 1986, 88]
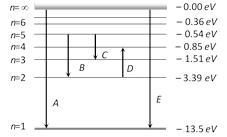
A)
First member of Lyman series, third spectral line of Balmer series and the second spectral line of Paschen series done
clear
B)
Ionization potential of hydrogen, second spectral line of Balmer series and third spectral line of Paschen series done
clear
C)
Series limit of Lyman series, third spectral line of Balmer series and second spectral line of Paschen series done
clear
D)
Series limit of Lyman series, second spectral line of Balmer series and third spectral line of Paschen series done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer9)
In the above figure D and E respectively represent [CPMT 1986, 88]
A)
Absorption line of Balmer series and the ionization potential of hydrogen done
clear
B)
Absorption line of Balmer series and the wavelength lesser than lowest of the Lyman series done
clear
C)
Spectral line of Balmer series and the maximum wavelength of Lyman series done
clear
D)
Spectral line of Lyman series and the absorption of greater wavelength of limiting value of Paschen series done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer10)
The Rutherford a-particle experiment shows that most of the a-particles pass through almost unscattered while some are scattered through large angles. What information does it give about the structure of the atom [AFMC 1997]
A)
Atom is hollow done
clear
B)
The whole mass of the atom is concentrated in a small centre called nucleus done
clear
C)
Nucleus is positively charged done
clear
D)
All the above done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer11)
Which of the following is true [MP PET 1993]
A)
Lyman series is a continuous spectrum done
clear
B)
Paschen series is a line spectrum in the infrared done
clear
C)
Balmer series is a line spectrum in the ultraviolet done
clear
D)
The spectral series formula can be derived from the Rutherford model of the hydrogen atom done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer12)
The energy required to knock out the electron in the third orbit of a hydrogen atom is equal to [DPMT 1987]
A)
\[13.6\ eV\] done
clear
B)
\[+\frac{13.6}{9}eV\] done
clear
C)
\[-\frac{13.6}{3}eV\] done
clear
D)
\[-\frac{3}{13.6}eV\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer13)
An electron has a mass of \[9.1\times {{10}^{-31}}kg\]. It revolves round the nucleus in a circular orbit of radius \[0.529\times {{10}^{-10}}metre\]at a speed of \[2.2\times {{10}^{6}}m/s\]. The magnitude of its linear momentum in this motion is [AFMC 1988]
A)
\[1.1\times {{10}^{-34}}kg-m/s\] done
clear
B)
\[2.0\times {{10}^{-24}}kg-m/s\] done
clear
C)
\[4.0\times {{10}^{-24}}kg-m/s\] done
clear
D)
\[4.0\times {{10}^{-31}}kg-m/s\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer14)
In a beryllium atom, if a0 be the radius of the first orbit, then the radius of the second orbit will be in general [CBSE PMT 1992; Roorkee 1993; BHU 1998]
A)
\[n{{a}_{0}}\] done
clear
B)
\[{{a}_{0}}\] done
clear
C)
\[{{n}^{2}}{{a}_{0}}\] done
clear
D)
\[\frac{{{a}_{0}}}{{{n}^{2}}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer15)
The ionization potential for second He electron is
A)
13.6 eV done
clear
B)
27.2 eV done
clear
C)
54.4 eV done
clear
D)
100 eV done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer16)
The energy required to remove an electron in a hydrogen atom from \[n=10\]state is [MP PMT 1993]
A)
13.6 eV done
clear
B)
1.36 eV done
clear
C)
0.136 eV done
clear
D)
0.0136 eV done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer17)
Every series of hydrogen spectrum has an upper and lower limit in wavelength. The spectral series which has an upper limit of wavelength equal to 18752 Å is [MP PMT 1993]
A)
Balmer series done
clear
B)
Lyman series done
clear
C)
Paschen series done
clear
D)
Pfund series (Rydberg constant \[R=1.097\times {{10}^{7}}\]per metre) done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer18)
The kinetic energy of the electron in an orbit of radius r in hydrogen atom is (e = electronic charge [MP PMT 1987]
A)
\[\frac{{{e}^{2}}}{{{r}^{2}}}\] done
clear
B)
\[\frac{{{e}^{2}}}{2r}\] done
clear
C)
\[\frac{{{e}^{2}}}{r}\] done
clear
D)
\[\frac{{{e}^{2}}}{2{{r}^{2}}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer19)
Ionization potential of hydrogen atom is 13.6 V. Hydrogen atoms in the ground state are excited by monochromatic radiation of photon energy 12.1 eV. The spectral lines emitted by hydrogen atoms according to Bohr's theory will be [CPMT 1990; CBSE PMT 1996; MP PMT 1999; AMU (Med.) 2002]
A)
One done
clear
B)
Two done
clear
C)
Three done
clear
D)
Four done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer20)
Energy levels A, B, C of a certain atom corresponding to increasing values of energy i.e. \[{{E}_{A}}<{{E}_{B}}<{{E}_{C}}\]. If \[{{\lambda }_{1}},\ {{\lambda }_{2}},\ {{\lambda }_{3}}\]are the wavelengths of radiations corresponding to the transitions C to B, B to A and C to A respectively, which of the following statements is correct [AIIMS 1995; CBSE PMT 1990, 2005]
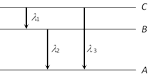
A)
\[{{\lambda }_{3}}={{\lambda }_{1}}+{{\lambda }_{2}}\] done
clear
B)
\[{{\lambda }_{3}}=\frac{{{\lambda }_{1}}{{\lambda }_{2}}}{{{\lambda }_{1}}+{{\lambda }_{2}}}\] done
clear
C)
\[{{\lambda }_{1}}+{{\lambda }_{2}}+{{\lambda }_{3}}=0\] done
clear
D)
\[\lambda _{3}^{2}=\lambda _{1}^{2}+\lambda _{2}^{2}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer21)
The angular momentum of electron in nth orbit is given by [Roorkee 1993]
A)
nh done
clear
B)
\[\frac{h}{2\pi n}\] done
clear
C)
\[n\frac{h}{2\pi }\] done
clear
D)
\[{{n}^{2}}\frac{h}{2\pi }\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer22)
The ratio of the energies of the hydrogen atom in its first to second excited state is [CPMT 1978]
A)
1/ 4 done
clear
B)
4/9 done
clear
C)
9/ 4 done
clear
D)
4 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer23)
An electron jumps from the 4th orbit to the 2nd orbit of hydrogen atom. Given the Rydberg's constant \[R={{10}^{5}}c{{m}^{-1}}\]. The frequency in Hz of the emitted radiation will be [CPMT 1976]
A)
\[\frac{3}{16}\times {{10}^{5}}\] done
clear
B)
\[\frac{3}{16}\times {{10}^{15}}\] done
clear
C)
\[\frac{9}{16}\times {{10}^{15}}\] done
clear
D)
\[\frac{3}{4}\times {{10}^{15}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer24)
The ionisation potential of hydrogen atom is 13.6 volt. The energy required to remove an electron in the n = 2 state of the hydrogen atom is [NCERT 1983; MP PET 2005]
A)
27.2 eV done
clear
B)
13.6eV done
clear
C)
6.8eV done
clear
D)
3.4eV done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer25)
The ionisation energy of 10 times ionised sodium atom is [DPMT 1991]
A)
13.6 eV done
clear
B)
\[13.6\times 11\ eV\] done
clear
C)
\[\frac{13.6}{11}eV\] done
clear
D)
\[13.6\times {{(11)}^{2}}eV\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer26)
If the wavelength of the first line of the Balmer series of hydrogen is\[6561\ {AA}\], the wavelength of the second line of the series should be [CPMT 1984; DPMT 2004]
A)
\[13122\ {AA}\] done
clear
B)
\[3280\ {AA}\] done
clear
C)
\[4860\ {AA}\] done
clear
D)
\[2187\ {AA}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer27)
The following diagram indicates the energy levels of a certain atom when the system moves from 2E level to E, a photon of wavelength \[\lambda \] is emitted. The wavelength of photon produced during its transition from \[\frac{4E}{3}\] level to E is [CPMT 1989]
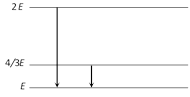
A)
\[\lambda /3\] done
clear
B)
\[3\lambda /4\] done
clear
C)
\[4\lambda /3\] done
clear
D)
\[3\lambda \] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer28)
A beam of fast moving alpha particles were directed towards a thin film of gold. The parts \[{A}',\ {B}'\]and \[{C}'\]of the transmitted and reflected beams corresponding to the incident parts A, B and C of the beam, are shown in the adjoining diagram. The number of alpha particles in [CPMT 1986, 88; RPET 2000]
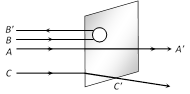
A)
\[{B}'\]will be minimum and in \[{C}'\]maximum done
clear
B)
\[{A}'\]will be maximum and in \[{B}'\]minimum done
clear
C)
\[{A}'\]will be minimum and in \[{B}'\]maximum done
clear
D)
\[{C}'\]will be minimum and in \[{B}'\]maximum done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer29)
According to Bohr's theory the radius of electron in an orbit described by principal quantum number n and atomic number Z is proportional to [CPMT 1988]
A)
\[{{Z}^{2}}{{n}^{2}}\] done
clear
B)
\[\frac{{{Z}^{2}}}{{{n}^{2}}}\] done
clear
C)
\[\frac{{{Z}^{2}}}{n}\] done
clear
D)
\[\frac{{{n}^{2}}}{Z}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer30)
The radius of electron's second stationary orbit in Bohr's atom is R. The radius of the third orbit will be [EAMCET 1992; DPMT 1999]
A)
3 R done
clear
B)
2.25 R done
clear
C)
9 R done
clear
D)
\[\frac{R}{3}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer31)
If m is mass of electron, v its velocity, r the radius of stationary circular orbit around a nucleus with charge Ze, then from Bohr's first postulate, the kinetic energy \[K=\frac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}\]of the electron in C.G.S. system is equal to [NCERT 1977]
A)
\[\frac{1}{2}\frac{Z{{e}^{2}}}{r}\] done
clear
B)
\[\frac{1}{2}\frac{Z{{e}^{2}}}{{{r}^{2}}}\] done
clear
C)
\[\frac{Z{{e}^{2}}}{r}\] done
clear
D)
\[\frac{Ze}{{{r}^{2}}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer32)
Consider an electron in the nth orbit of a hydrogen atom in the Bohr model. The circumference of the orbit can be expressed in terms of the de Broglie wavelength \[\lambda \]of that electron as [CBSE PMT 1990]
A)
\[(0.259)\ n\lambda \] done
clear
B)
\[\sqrt{n}\lambda \] done
clear
C)
\[(13.6)\ \lambda \] done
clear
D)
\[n\lambda \] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer33)
In any Bohr orbit of the hydrogen atom, the ratio of kinetic energy to potential energy of the electron is [MP PET 1994]
A)
1/2 done
clear
B)
2 done
clear
C)
\[-1/2\] done
clear
D)
? 2 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer34)
The spectral series of the hydrogen spectrum that lies in the ultraviolet region is the [CPMT 1990; MP PET 1994; MP PMT 2000]
A)
Balmer series done
clear
B)
Pfund series done
clear
C)
Paschen series done
clear
D)
Lyman series done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer35)
Figure shows the energy levels P, Q, R, S and G of an atom where G is the ground state. A red line in the emission spectrum of the atom can be obtained by an energy level change from Q to S. A blue line can be obtained by following energy level change [MP PMT 1994]
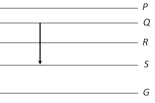
A)
P to Q done
clear
B)
Q to R done
clear
C)
R to S done
clear
D)
R to G done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer36)
A hydrogen atom (ionisation potential 13.6 eV) makes a transition from third excited state to first excited state. The energy of the photon emitted in the process is [MNR 1995]
A)
1.89 eV done
clear
B)
2.55 eV done
clear
C)
12.09 eV done
clear
D)
12.75 Ev done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer37)
The figure indicates the energy level diagram of an atom and the origin of six spectral lines in emission (e.g. line no. 5 arises from the transition from level B to A). The following spectral lines will also occur in the absorption spectrum [CBSE PMT 1995]
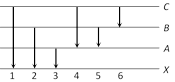
A)
1, 4, 6 done
clear
B)
4, 5, 6 done
clear
C)
1, 2, 3 done
clear
D)
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer38)
When a hydrogen atom is raised from the ground state to an excited state [CBSE PMT 1995; AMU (Med.) 1999]
A)
P.E. increases and K.E. decreases done
clear
B)
P.E. decreases and K.E. increases done
clear
C)
Both kinetic energy and potential energy increase done
clear
D)
Both K.E. and P.E. decrease done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer39)
An electron makes a transition from orbit n = 4 to the orbit n = 2 of a hydrogen atom. The wave number of the emitted radiations (R = Rydberg's constant) will be [CBSE PMT 1995]
A)
\[\frac{16}{3R}\] done
clear
B)
\[\frac{2R}{16}\] done
clear
C)
\[\frac{3R}{16}\] done
clear
D)
\[\frac{4R}{16}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer40)
In Bohr model of the hydrogen atom, the lowest orbit corresponds to [Manipal MEE 1995]
A)
Infinite energy done
clear
B)
The maximum energy done
clear
C)
The minimum energy done
clear
D)
Zero energy done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer41)
The ratio of the kinetic energy to the total energy of an electron in a Bohr orbit is [Roorkee 1995; BHU 2002]
A)
? 1 done
clear
B)
2 done
clear
C)
1 : 2 done
clear
D)
None of these done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer42)
An electron in the n = 1 orbit of hydrogen atom is bound by 13.6 eV. If a hydrogen atom is in the n = 3 state, how much energy is required to ionize it [MP PMT 1995]
A)
13.6 eV done
clear
B)
4.53 eV done
clear
C)
3.4 eV done
clear
D)
1.51 eV done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer43)
Which of the following statements about the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom is false [MP PMT 1995]
A)
Acceleration of electron in n = 2 orbit is less than that in n = 1 orbit done
clear
B)
Angular momentum of electron in n = 2 orbit is more than that in n = 1 orbit done
clear
C)
Kinetic energy of electron in n = 2 orbit is less than that in n = 1 orbit done
clear
D)
Potential energy of electron in n = 2 orbit is less than that in n = 1 orbit done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer44)
If an electron jumps from 1st orbital to 3rd orbital, then it will [AFMC 1996]
A)
Absorb energy done
clear
B)
Release energy done
clear
C)
No gain of energy done
clear
D)
None of these done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer45)
The ratio of the frequencies of the long wavelength limits of Lyman and Balmer series of hydrogen spectrum is [KCEE 1996]
A)
27 : 5 done
clear
B)
5 : 27 done
clear
C)
4 : 1 done
clear
D)
1 : 4 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer46)
Which of the following transitions in a hydrogen atom emits photon of the highest frequency [MP PET 1996; DPMT 2001]
A)
n = 1 to n = 2 done
clear
B)
n = 2 to n = 1 done
clear
C)
n = 2 to n = 6 done
clear
D)
n = 6 to n = 2 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer47)
In terms of Rydberg's constant R, the wave number of the first Balmer line is [MP PMT 1996]
A)
R done
clear
B)
3R done
clear
C)
\[\frac{5R}{36}\] done
clear
D)
\[\frac{8R}{9}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer48)
If the ionisation potential of helium atom is 24.6 volt, the energy required to ionise it will be [MP PMT 1996]
A)
24.6 eV done
clear
B)
24.6 V done
clear
C)
13.6 V done
clear
D)
13.6 eV done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer49)
Which of the transitions in hydrogen atom emits a photon of lowest frequency (n = quantum number) [BHU 1999]
A)
n = 2 to n = 1 done
clear
B)
n = 4 to n = 3 done
clear
C)
n = 3 to n = 1 done
clear
D)
n = 4 to n = 2 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer50)
According to Bohr's theory, the expressions for the kinetic and potential energy of an electron revolving in an orbit is given respectively by
A)
\[+\frac{{{e}^{2}}}{8\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}r}\]and \[-\frac{{{e}^{2}}}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}r}\] done
clear
B)
\[+\frac{8\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}{{e}^{2}}}{r}\]and\[-\frac{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}{{e}^{2}}}{r}\] done
clear
C)
\[-\frac{{{e}^{2}}}{8\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}r}\]and \[-\frac{{{e}^{2}}}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}r}\] done
clear
D)
\[+\frac{{{e}^{2}}}{8\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}r}\]and \[+\frac{{{e}^{2}}}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}r}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer51)
In a hydrogen atom, which of the following electronic transitions would involve the maximum energy change [MP PET 1997]
A)
From n = 2 to n = 1 done
clear
B)
From n = 3 to n = 1 done
clear
C)
From n = 4 to n = 2 done
clear
D)
From n = 3 to n = 2 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer52)
In the lowest energy level of hydrogen atom, the electron has the angular momentum [MP PET 1997; BCECE 2003]
A)
\[\pi /h\] done
clear
B)
\[h/\pi \] done
clear
C)
\[h/2\pi \] done
clear
D)
\[2\pi /h\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer53)
The minimum energy required to excite a hydrogen atom from its ground state is [EAMCET (Engg.) 1995; MP PMT 1997; CPMT 1999; DCE 1999]
A)
13.6 eV done
clear
B)
\[-13.6\ eV\] done
clear
C)
3.4eV done
clear
D)
10.2 eV done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer54)
Ratio of the wavelengths of first line of Lyman series and first line of Balmer series is [EAMCET (Engg.) 1995; MP PMT 1997]
A)
1: 3 done
clear
B)
27 : 5 done
clear
C)
5 : 27 done
clear
D)
4 : 9 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer55)
The Rydberg constant R for hydrogen is [MP PMT/PET 1998]
A)
\[R=-\left( \frac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}} \right).\frac{2{{\pi }^{2}}m{{e}^{2}}}{c{{h}^{2}}}\] done
clear
B)
\[R=\left( \frac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}} \right).\frac{2{{\pi }^{2}}m{{e}^{4}}}{c{{h}^{2}}}\] done
clear
C)
\[R={{\left( \frac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}} \right)}^{2}}.\frac{2{{\pi }^{2}}m{{e}^{4}}}{{{c}^{2}}{{h}^{2}}}\] done
clear
D)
\[R={{\left( \frac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}} \right)}^{2}}.\frac{2{{\pi }^{2}}m{{e}^{4}}}{c{{h}^{3}}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer56)
The wavelength of the first line of Balmer series is \[6563\ {AA}\]. The Rydberg constant for hydrogen is about [MP PMT/PET 1998]
A)
\[1.09\times {{10}^{7}}per\ m\] done
clear
B)
\[1.09\times {{10}^{8}}per\ m\] done
clear
C)
\[1.09\times {{10}^{9}}per\ m\] done
clear
D)
\[1.09\times {{10}^{5}}per\ m\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer57)
According to Bohr's theory the moment of momentum of an electron revolving in second orbit of hydrogen atom will be [MP PET 1999; KCET 2003]
A)
\[2\pi h\] done
clear
B)
\[\pi h\] done
clear
C)
\[\frac{h}{\pi }\] done
clear
D)
\[\frac{2h}{\pi }\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer58)
The velocity of an electron in the second orbit of sodium atom (atomic number = 11) is v. The velocity of an electron in its fifth orbit will be [MP PET 1999]
A)
v done
clear
B)
\[\frac{22}{5}v\] done
clear
C)
\[\frac{5}{2}v\] done
clear
D)
\[\frac{2}{5}v\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer59)
The absorption transitions between the first and the fourth energy states of hydrogen atom are 3. The emission transitions between these states will be [MP PET 1999]
A)
3 done
clear
B)
4 done
clear
C)
5 done
clear
D)
6 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer60)
The ratio of longest wavelength and the shortest wavelength observed in the five spectral series of emission spectrum of hydrogen is [MP PET 1999]
A)
\[\frac{4}{3}\] done
clear
B)
\[\frac{525}{376}\] done
clear
C)
25 done
clear
D)
\[\frac{900}{11}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer61)
In the Bohr model of a hydrogen atom, the centripetal force is furnished by the coulomb attraction between the proton and the electron. If \[{{a}_{0}}\]is the radius of the ground state orbit, m is the mass, e is the charge on the electron and \[{{\varepsilon }_{0}}\]is the vacuum permittivity, the speed of the electron is [CBSE PMT 1998]
A)
0 done
clear
B)
\[_{7}{{N}^{14}}\] done
clear
C)
\[\frac{1}{4}\] done
clear
D)
\[\frac{\sqrt{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}{{a}_{0}}m}}{e}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer62)
The electron in a hydrogen atom makes a transition\[{{n}_{1}}\to {{n}_{2}}\], where \[{{n}_{1}}\] and \[{{n}_{2}}\] are the principal quantum numbers of the two states. Assume the Bohr model to be valid. The time period of the electron in the initial state is eight times that in the final state. The possible values of n1 and n2 are [IIT 1998; KCET 2005]
A)
\[{{n}_{1}}=4,\ {{n}_{2}}=2\] done
clear
B)
\[{{n}_{1}}=8,\ {{n}_{2}}=2\] done
clear
C)
\[{{n}_{1}}=8,\ {{n}_{2}}=1\] done
clear
D)
\[{{n}_{1}}=6,\ {{n}_{2}}=3\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer63)
As per Bohr model, the minimum energy (in eV) required to remove an electron from the ground state of doubly ionized Li atom (Z = 3) is [IIT 1997 Re-Exam; MH CET 2000]
A)
1.51 done
clear
B)
13.6 done
clear
C)
40.8 done
clear
D)
122.4 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer64)
Which one of these is non-divisible [KCET 1994]
A)
Nucleus done
clear
B)
Photon done
clear
C)
Proton done
clear
D)
Atom done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer65)
In Bohr's model of hydrogen atom, let PE represents potential energy and TE the total energy. In going to a higher level [KCET 1994]
A)
PE decreases, TE increases done
clear
B)
PE increases, TE increases done
clear
C)
PE decreases, TE decreases done
clear
D)
PE increases, TE decreases done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer66)
According to Bohr's model, the radius of the second orbit of helium atom is [Bihar MEE 1995]
A)
0.53 Å done
clear
B)
1.06 Å done
clear
C)
2.12 Å done
clear
D)
0.265 Å done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer67)
The fact that photons carry energy was established by [ISM Dhanbad 1994]
A)
Doppler's effect done
clear
B)
Compton's effect done
clear
C)
Bohr's theory done
clear
D)
Diffraction of light done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer68)
An ionic atom equivalent to hydrogen atom has wavelength equal to 1/4 of the wavelengths of hydrogen lines. The ion will be [RPET 1997]
A)
\[H{{e}^{+}}\] done
clear
B)
\[L{{i}^{++}}\] done
clear
C)
\[N{{e}^{9+}}\] done
clear
D)
\[N{{a}^{10+}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer69)
The extreme wavelengths of Paschen series are [RPET 1997]
A)
\[0.365\mu m\]and \[0.565\mu m\] done
clear
B)
\[0.818\mu m\]and \[1.89\mu m\] done
clear
C)
\[1.45\mu m\]and \[4.04\mu m\] done
clear
D)
\[2.27\mu m\]and \[7.43\mu m\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer70)
The third line of Balmer series of an ion equivalent to hydrogen atom has wavelength of 108.5 nm. The ground state energy of an electron of this ion will be [RPET 1997]
A)
3.4 eV done
clear
B)
13.6 eV done
clear
C)
54.4 eV done
clear
D)
122.4 eV done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer71)
An electron in the n = 1 orbit of hydrogen atom is bound by 13.6 eV energy is required to ionize it is [MP PMT 2003]
A)
13.6 eV done
clear
B)
6.53 eV done
clear
C)
5.4 eV done
clear
D)
1.51 eV done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer72)
Ionization energy of hydrogen is 13.6 eV. If \[h=6.6\times {{10}^{-34}}J-\]sec, the value of R will be of the order of [RPMT 1997]
A)
\[{{10}^{10}}{{m}^{-1}}\] done
clear
B)
\[{{10}^{7}}{{m}^{-1}}\] done
clear
C)
\[{{10}^{4}}{{m}^{-1}}\] done
clear
D)
\[{{10}^{-7}}{{m}^{-1}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer73)
To explain his theory, Bohr used [CBSE PMT1993; MP PET 2002]
A)
Conservation of linear momentum done
clear
B)
Conservation of angular momentum done
clear
C)
Conservation of quantum frequency done
clear
D)
Conservation of energy done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer74)
The ionisation energy of hydrogen atom is 13.6 eV. Following Bohr's theory, the energy corresponding to a transition between the 3rd and the 4th orbit is [CBSE PMT 1992; DPMT 2000; RPMT 1999; AMU (Med.) 2001]
A)
3.40 eV done
clear
B)
1.51 eV done
clear
C)
0.85 eV done
clear
D)
0.66 eV done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer75)
Hydrogen atoms are excited from ground state of the principal quantum number 4. Then the number of spectral lines observed will be [CBSE PMT 1993]
A)
3 done
clear
B)
6 done
clear
C)
5 done
clear
D)
2 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer76)
Hydrogen atom emits blue light when it changes from n = 4 energy level to the n = 2 level. Which colour of light would the atom emit when it changes from the n = 5 level to the n = 2 level [KCET 1993]
A)
Red done
clear
B)
Yellow done
clear
C)
Green done
clear
D)
Violet done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer77)
In Rutherford scattering experiment, what will be the correct angle for \[\alpha \] scattering for an impact parameter b = 0 [CBSE PMT 1994; JIPMER 2000]
A)
\[{{90}^{o}}\] done
clear
B)
\[{{270}^{o}}\] done
clear
C)
\[{{0}^{o}}\] done
clear
D)
\[{{180}^{o}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer78)
The radius of hydrogen atom in its ground state is \[5.3\times {{10}^{-11}}m\]. After collision with an electron it is found to have a radius of \[21.2\times {{10}^{-11}}m\]. What is the principal quantum number n of the final state of the atom [CBSE PMT 1994; CPMT 2001; MH CET 2000]
A)
n = 4 done
clear
B)
n = 2 done
clear
C)
n = 16 done
clear
D)
n = 3 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer79)
The splitting of line into groups under the effect of electric or magnetic field is called [AFMC 1995]
A)
Zeeman's effect done
clear
B)
Bohr's effect done
clear
C)
Heisenberg's effect done
clear
D)
Magnetic effect done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer80)
The energy of a hydrogen atom in its ground state is \[-13.6\ eV\]. The energy of the level corresponding to the quantum number n = 2 (first excited state) in the hydrogen atom is [CBSE PMT 1996; CBSE PMT 1997, 2001; MP PET 2000; AFMC 2000, 01, 02; BCECE 2003]
A)
? 2.72 eV done
clear
B)
? 0.85 eV done
clear
C)
? 0.54 eV done
clear
D)
? 3.4 eV done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer81)
The first line of Balmer series has wavelength 6563 Å. What will be the wavelength of the first member of Lyman series [RPMT 1996]
A)
1215.4 Å done
clear
B)
2500 Å done
clear
C)
7500 Å done
clear
D)
600 Å done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer82)
The wavelength of Lyman series is [BHU 1997]
A)
\[\frac{4}{3\times 10967}cm\] done
clear
B)
\[\frac{3}{4\times 10967}cm\] done
clear
C)
\[\frac{4\times 10967}{3}cm\] done
clear
D)
\[\frac{3}{4}\times 10967\ cm\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer83)
When hydrogen atom is in its first excited level, its radius is .... its ground state radius [CBSE PMT 1997]
A)
Half done
clear
B)
Same done
clear
C)
Twice done
clear
D)
Four times done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer84)
Hydrogen atom excites energy level from fundamental state to n = 3. Number of spectrum lines according to Bohr, is [CPMT 1997]
A)
4 done
clear
B)
3 done
clear
C)
1 done
clear
D)
2 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer85)
Number of spectral lines in hydrogen atom is [CPMT 1997]
A)
3 done
clear
B)
6 done
clear
C)
15 done
clear
D)
Infinite done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer86)
In Bohr's model, the atomic radius of the first orbit is \[{{r}_{0}}\], then the radius of the third orbit is [AIIMS 1997; CPMT 2001; KCET (Engg./Med.) 1999; Pb. PMT 2004]
A)
\[\frac{{{r}_{0}}}{9}\] done
clear
B)
\[{{r}_{0}}\] done
clear
C)
\[9{{r}_{0}}\] done
clear
D)
\[3{{r}_{0}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer87)
The wavelength of the energy emitted when electron come from fourth orbit to second orbit in hydrogen is \[20.397\,cm\]. The wavelength of energy for the same transition in \[H{{e}^{+}}\]is [AIIMS 1997; JIPMER 2000]
A)
\[5.099\ c{{m}^{-1}}\] done
clear
B)
\[20.497\ c{{m}^{-1}}\] done
clear
C)
\[40.994\ c{{m}^{-1}}\] done
clear
D)
\[81.988\ c{{m}^{-1}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer88)
Minimum excitation potential of Bohr's first orbit in hydrogen atom is [BHU 1998; JIPMER 2001, 02; Pb. PMT 2004]
A)
13.6 V done
clear
B)
3.4 V done
clear
C)
10.2 V done
clear
D)
3.6 V done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer89)
Which of the following statements are true regarding Bohr's model of hydrogen atom (I) Orbiting speed of electron decreases as it shifts to discrete orbits away from the nucleus (II) Radii of allowed orbits of electron are proportional to the principal quantum number (III) Frequency with which electrons orbits around the nucleus in discrete orbits is inversely proportional to the principal quantum number (IV) Binding force with which the electron is bound to the nucleus increases as it shifts to outer orbits Select correct answer using the codes given below Codes : [SCRA 1998]
A)
I and III done
clear
B)
II and IV done
clear
C)
I, II and III done
clear
D)
II, III and IV done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer90)
The wavelength of radiation emitted is \[{{\lambda }_{0}}\]when an electron jumps from the third to the second orbit of hydrogen atom. For the electron jump from the fourth to the second orbit of the hydrogen atom, the wavelength of radiation emitted will be [SCRA 1998; MP PET 2001; MH CET 2003]
A)
\[\frac{16}{25}{{\lambda }_{0}}\] done
clear
B)
\[\frac{20}{27}{{\lambda }_{0}}\] done
clear
C)
\[\frac{27}{20}{{\lambda }_{0}}\] done
clear
D)
\[\frac{25}{16}{{\lambda }_{0}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer91)
For electron moving in nth orbit of H-atom the angular velocity is proportional to [RPET 1999]
A)
n done
clear
B)
1/n done
clear
C)
n3 done
clear
D)
1/n3 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer92)
The energy of electron in first excited state of H-atom is \[-\ 3.4\ eV\] its kinetic energy is [RPET 1999; CBSE PMT 2005]
A)
? 3.4 eV done
clear
B)
+ 3.4 eV done
clear
C)
? 6.8 eV done
clear
D)
6.8 eV done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer93)
The energy required to excite an electron from the ground state of hydrogen atom to the first excited state, is [Pb. PMT 1999]
A)
\[1.602\times {{10}^{-14}}\,J\] done
clear
B)
\[1.619\times {{10}^{-16}}\,J\] done
clear
C)
\[1.632\times {{10}^{-18}}J\] done
clear
D)
\[1.656\times {{10}^{-20}}J\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer94)
Which of the following phenomena suggests the presence of electron energy levels in atoms [JIPMER 1999]
A)
Radioactive decay done
clear
B)
Isotopes done
clear
C)
Spectral lines done
clear
D)
a-particles scattering done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer95)
Which of the following spectral series in hydrogen atom give spectral line of 4860 Å [Roorkee 1999]
A)
Lyman done
clear
B)
Balmer done
clear
C)
Paschen done
clear
D)
Brackett done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer96)
If scattering particles are 56 for \[{{90}^{o}}\] angle then this will be at \[{{60}^{o}}\] angle [RPMT 2000]
A)
224 done
clear
B)
256 done
clear
C)
98 done
clear
D)
108 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer97)
When an electron in hydrogen atom is excited, from its 4th to 5th stationary orbit, the change in angular momentum of electron is (Planck?s constant: \[h=6.6\times {{10}^{-34}}J\text{-s}\]) [AFMC 2000; Pb. PET 2001]
A)
\[4.16\times {{10}^{-34}}\,J\text{-}s\] done
clear
B)
\[3.32\times {{10}^{-34}}\,J\text{-}s\] done
clear
C)
\[1.05\times {{10}^{-34}}\,J\text{-}s\] done
clear
D)
\[2.08\times {{10}^{-34}}\,J\text{-}s\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer98)
Energy of electron in a orbit of H-atom is [RPET 2000]
A)
Positive done
clear
B)
Negative done
clear
C)
Zero done
clear
D)
Nothing can be said done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer99)
The concept of stationary orbits was proposed by [Pb. PMT 2000]
A)
Neil Bohr done
clear
B)
J.J. Thomson done
clear
C)
Ruther ford done
clear
D)
I. Newton done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer100)
In a hydrogen atom, the distance between the electron and proton is \[2.5\times {{10}^{-11}}\,m\]. The electrical force of attraction between them will be [Pb. PMT 2000]
A)
\[2.8\times {{10}^{-7}}\,N\] done
clear
B)
\[3.7\times {{10}^{-7}}N\] done
clear
C)
\[6.2\times {{10}^{-7}}N\] done
clear
D)
\[9.1\times {{10}^{-7}}N\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer101)
If \[{{\lambda }_{\text{max}}}\] is 6563 Å, then wave length of second line for Balmer series will be [RPMT 2000]
A)
\[\lambda =\frac{16}{3R}\] done
clear
B)
\[\lambda =\frac{36}{5R}\] done
clear
C)
\[\lambda =\frac{4}{3R}\] done
clear
D)
None of the above done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer102)
What will be the angular momentum of a electron, if energy of this electron in H-atom is 1.5eV (in J-sec) [RPMT 2000]
A)
\[1.05\times {{10}^{-34}}\] done
clear
B)
\[2.1\times {{10}^{-34}}\] done
clear
C)
\[3.15\times {{10}^{-34}}\] done
clear
D)
\[-2.1\times {{10}^{-34}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer103)
Who discovered spin quantum number [RPMT 2000]
A)
Unlenbeck and Goudsmit done
clear
B)
Nell?s Bohr done
clear
C)
Zeeman done
clear
D)
Sommerfield done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer104)
The time of revolution of an electron around a nucleus of charge Ze in nth Bohr orbit is directly proportional to [MP PET 2003]
A)
n done
clear
B)
\[\frac{{{n}^{3}}}{{{Z}^{2}}}\] done
clear
C)
\[\frac{{{n}^{2}}}{Z}\] done
clear
D)
\[\frac{Z}{n}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer105)
In Bohr?s model, if the atomic radius of the first orbit is \[{{r}_{0}}\], then the radius of the fourth orbit is [CBSE PMT 2000]
A)
\[{{r}_{0}}\] done
clear
B)
\[4{{r}_{0}}\] done
clear
C)
\[{{r}_{0}}/16\] done
clear
D)
\[16{{r}_{0}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer106)
If R is the Rydberg?s constant for hydrogen the wave number of the first line in the Lyman series will be [KCET 2000]
A)
\[\frac{R}{4}\] done
clear
B)
\[\frac{3R}{4}\] done
clear
C)
\[\frac{R}{2}\] done
clear
D)
2R done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer107)
In hydrogen atom, if the difference in the energy of the electron in \[n=2\] and \[n=3\] orbits is E, the ionization energy of hydrogen atom is [EAMCET (Med.) 2000]
A)
13.2 E done
clear
B)
7.2 E done
clear
C)
5.6 E done
clear
D)
3.2 E done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer108)
The first member of the Paschen series in hydrogen spectrum is of wavelength 18,800 Å. The short wavelengths limit of Paschen series is [EAMCET (Med.) 2000]
A)
1215 Å done
clear
B)
6560 Å done
clear
C)
8225 Å done
clear
D)
12850 Å done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer109)
The ratio of the largest to shortest wavelengths in Lyman series of hydrogen spectra is [EAMCET (Med.) 2000]
A)
\[\frac{25}{9}\] done
clear
B)
\[\frac{17}{6}\] done
clear
C)
\[\frac{9}{5}\] done
clear
D)
\[\frac{4}{3}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer110)
In Bohr model of hydrogen atom, the ratio of periods of revolution of an electron in \[n=2\] and \[n=1\] orbits is [EAMCET (Engg.) 2000]
A)
2 : 1 done
clear
B)
4 : 1 done
clear
C)
8 : 1 done
clear
D)
16 : 1 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer111)
The ratio of the longest to shortest wavelengths in Brackett series of hydrogen spectra is [EAMCET (Engg.) 2000]
A)
\[\frac{25}{9}\] done
clear
B)
\[\frac{17}{6}\] done
clear
C)
\[\frac{9}{5}\] done
clear
D)
\[\frac{4}{3}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer112)
The electron in a hydrogen atom makes a transition from an excited state to the ground state. Which of the following statements is true [IIT JEE (Screening) 2000]
A)
Its kinetic energy increases and its potential and total energies decrease done
clear
B)
Its kinetic energy decreases, potential energy increases and its total energy remains the same done
clear
C)
Its kinetic and total energies decrease and its potential energy increases done
clear
D)
Its kinetic, potential and total energies decreases done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer113)
The ratio of minimum to maximum wavelength in Balmer series is [MP PET 2000]
A)
5 : 9 done
clear
B)
5 : 36 done
clear
C)
1 : 4 done
clear
D)
3 : 4 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer114)
The radius of the Bohr orbit in the ground state of hydrogen atom is 0.5 Å. The radius of the orbit of the electron in the third excited state of \[H{{e}^{+}}\] will be [MP PMT 2000]
A)
8 Å done
clear
B)
4 Å done
clear
C)
0.5 Å done
clear
D)
0.25 Å done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer115)
The ratio of the speed of the electron in the first Bohr orbit of hydrogen and the speed of light is equal to (where e, h and c have their usual meanings) [MP PMT 2000]
A)
\[2\pi hc/{{e}^{2}}\] done
clear
B)
\[{{e}^{2}}h/2\pi c\] done
clear
C)
\[{{e}^{2}}c/2\pi h\] done
clear
D)
\[2\pi {{e}^{2}}/hc\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer116)
According to the Rutherford?s atomic model, the electrons inside the atom are [KCET (Med.) 2000]
A)
Stationary done
clear
B)
Not stationary done
clear
C)
Centralized done
clear
D)
None of these done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer117)
The energy of hydrogen atom in its ground state is ? 13.6 eV. The energy of the level corresponding to the quantum number n is equal 5 is [KCET (Engg./Med.) 2001]
A)
? 5.40 eV done
clear
B)
? 2.72 eV done
clear
C)
? 0.85 eV done
clear
D)
? 0.54 eV done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer118)
According to classical theory, the circular path of an electron in Rutherford atom is [BHU 2001]
A)
Spiral done
clear
B)
Circular done
clear
C)
Parabolic done
clear
D)
Straight line done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer119)
Rutherford?s a-particle experiment showed that the atoms have [AFMC 2001]
A)
Proton done
clear
B)
Nucleus done
clear
C)
Neutron done
clear
D)
Electrons done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer120)
Orbital acceleration of electron is [RPET 2001]
A)
\[\frac{{{n}^{2}}{{h}^{2}}}{4{{\pi }^{2}}{{m}^{2}}{{r}^{3}}}\] done
clear
B)
\[\frac{{{n}^{2}}{{h}^{2}}}{2{{n}^{2}}{{r}^{3}}}\] done
clear
C)
\[\frac{4{{n}^{2}}{{h}^{2}}}{{{\pi }^{2}}{{m}^{2}}{{r}^{3}}}\] done
clear
D)
\[\frac{4{{n}^{2}}{{h}^{2}}}{4{{\pi }^{2}}{{m}^{2}}{{r}^{3}}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer121)
Which of the following is true for number of spectral lines in going form Layman series to Pfund series [RPET 2001]
A)
Increases done
clear
B)
Decreases done
clear
C)
Unchanged done
clear
D)
May decreases or increases done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer122)
The wavelength of yellow line of sodium is 5896 Å. Its wave number will be [MP PET 2001]
A)
50883 × 1010 per second done
clear
B)
16961 per cm done
clear
C)
17581 per cm done
clear
D)
50883 per cm done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer123)
Radius of the first orbit of the electron in a hydrogen atom is 0.53 Å. So, the radius of the third orbit will be [Kerala (Engg.) 2001]
A)
2.12 Å done
clear
B)
4.77 Å done
clear
C)
1.06 Å done
clear
D)
1.59 Å done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer124)
The first line in the Lyman series has wavelength l. The wavelength of the first line in Balmer series is [MH CET (Med.) 2001]
A)
\[\frac{2}{9}\,\lambda \] done
clear
B)
\[\frac{9}{2}\,\lambda \] done
clear
C)
\[\frac{5}{27}\,\lambda \] done
clear
D)
\[\frac{27}{5}\lambda \] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer125)
In hydrogen atom which quantity is integral multiple of \[\frac{h}{2\pi }\] [DCE 2001]
A)
Angular momentum done
clear
B)
Angular velocity done
clear
C)
Angular acceleration done
clear
D)
Momentum done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer126)
In the following transitions, which one has higher frequency [UPSEAT 2001]
A)
3 ? 2 done
clear
B)
4 ? 3 done
clear
C)
4 ? 2 done
clear
D)
3 ? 1 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer127)
The diagram shows the path of four a-particles of the same energy being scattered by the nucleus of an atom simultaneously. Which of these are/is not physically possible [AMU (Med.) 2001]
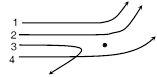
A)
3 and 4 done
clear
B)
2 and 3 done
clear
C)
1 and 4 done
clear
D)
4 only done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer128)
An electron jumps from 5th orbit to 4th orbit of hydrogen atom. Taking the Rydberg constant as \[{{10}^{7}}\] per metre. What will be the frequency of radiation emitted [Pb. PMT 2001]
A)
\[6.75\times {{10}^{12}}\,Hz\] done
clear
B)
\[6.75\times {{10}^{14}}\,Hz\] done
clear
C)
\[6.75\times {{10}^{13}}\,Hz\] done
clear
D)
None of these done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer129)
For principal quantum number \[n=3\], the possible values of orbital quantum number ?l? are [MP PET 2001; MP PMT 2001]
A)
1, 2, 3 done
clear
B)
0, 1, 2, 3 done
clear
C)
0, 1, 2 done
clear
D)
?1, 0, +1 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer130)
Four lowest energy levels of H-atom are shown in the figure. The number of possible emission lines would be [MP PMT 2001]

A)
3 done
clear
B)
4 done
clear
C)
5 done
clear
D)
6 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer131)
The order of the size of nucleus and Bohr radius of an atom respectively are [MP PET 2001; MP PMT 2001]
A)
\[{{10}^{-14}}m,\ {{10}^{-10}}m\] done
clear
B)
\[{{10}^{-10}}\,m,\,{{10}^{-8}}\,m\] done
clear
C)
\[{{10}^{-20}}m,\ {{10}^{-16}}m\] done
clear
D)
\[{{10}^{-8}}\,m,\,{{10}^{-6}}\,m\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer132)
Energy of an electron in an excited hydrogen atom is ? 3.4 eV. Its angular momentum will be: \[h=6.626\times {{10}^{-34}}J-s\] [UPSEAT 1999; Kerala PET 2002]
A)
\[1.11\times {{10}^{34}}J\ \sec \] done
clear
B)
\[1.51\times {{10}^{-31}}J\ \sec \] done
clear
C)
\[2.11\times {{10}^{-34}}J\ \sec \] done
clear
D)
\[3.72\times {{10}^{-34}}J\ \sec \] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer133)
The ratio of the wavelengths for 2 ® 1 transition in Li++, He+ and H is [UPSEAT 2003]
A)
1 : 2 : 3 done
clear
B)
1 : 4 : 9 done
clear
C)
4 : 9 : 36 done
clear
D)
3 : 2 : 1 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer134)
The wavelength of light emitted from second orbit to first orbits in a hydrogen atom is [Pb. PMT 2002]
A)
\[1.215\times {{10}^{-7}}m\] done
clear
B)
\[1.215\times {{10}^{-5}}m\] done
clear
C)
\[1.215\times {{10}^{-4}}m\] done
clear
D)
\[1.215\times {{10}^{-3}}m\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer135)
Energy of the electron in nth orbit of hydrogen atom is given by \[{{E}_{n}}=-\frac{13.6}{{{n}^{2}}}eV\]. The amount of energy needed to transfer electron from first orbit to third orbit is [MH CET 2002; Kerala PMT 2002]
A)
13.6 eV done
clear
B)
3.4 eV done
clear
C)
12.09 eV done
clear
D)
1.51 eV done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer136)
The ratio of speed of an electron in ground state in Bohrs first orbit of hydrogen atom to velocity of light in air is [MH CET 2002]
A)
\[\frac{{{e}^{2}}}{2{{\varepsilon }_{0}}hc}\] done
clear
B)
\[\frac{2{{e}^{2}}{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}{hc}\] done
clear
C)
\[\frac{{{e}^{3}}}{2{{\varepsilon }_{0}}hc}\] done
clear
D)
\[\frac{2{{\varepsilon }_{0}}hc}{{{e}^{2}}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer137)
Whenever a hydrogen atom emits a photon in the Balmer series [KCET 2002]
A)
It need not emit any more photon done
clear
B)
It may emit another photon in the Paschen series done
clear
C)
It must emit another photon in the Lyman series done
clear
D)
It may emit another photon in the Balmer series done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer138)
The de-Broglie wavelength of an electron in the first Bohr orbit is [KCET 2002]
A)
Equal to one fourth the circumference of the first orbit done
clear
B)
Equal to half the circumference of the first orbit done
clear
C)
Equal to twice the circumference of the first orbit done
clear
D)
Equal to the circumference of the first orbit done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer139)
In hydrogen atom, when electron jumps from second to first orbit, then energy emitted is [AIEEE 2002]
A)
? 13.6 eV done
clear
B)
? 27.2 eV done
clear
C)
? 6.8 eV done
clear
D)
None of these done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer140)
Minimum energy required to takeout the only one electron from ground state of \[H{{e}^{+}}\] is [CPMT 2002]
A)
13.6 eV done
clear
B)
54.4 eV done
clear
C)
27.2 eV done
clear
D)
6.8 eV done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer141)
The frequency of 1st line of Balmer series in \[{{H}_{2}}\] atom is \[{{\nu }_{0}}\]. The frequency of line emitted by singly ionised He atom is [CPMT 2002]
A)
\[2{{\nu }_{0}}\] done
clear
B)
\[4{{\nu }_{0}}\] done
clear
C)
\[{{\nu }_{0}}/2\] done
clear
D)
\[{{\nu }_{0}}/4\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer142)
When the electron in the hydrogen atom jumps from 2nd orbit to 1st orbit, the wavelength of radiation emitted is l. When the electrons jump from 3rd orbit to 1st orbit, the wavelength of emitted radiation would be [MP PMT 2002]
A)
\[\frac{27}{32}\lambda \] done
clear
B)
\[\frac{32}{27}\lambda \] done
clear
C)
\[\frac{2}{3}\lambda \] done
clear
D)
\[\frac{3}{2}\lambda \] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer143)
The possible quantum number for 3d electron are [MP PMT 2002]
A)
\[n=3,\,l=1,\,{{m}_{l}}=+1,\,{{m}_{s}}=-\frac{1}{2}\] done
clear
B)
\[n=3,\,l=2,\,{{m}_{l}}=+2,\,{{m}_{s}}=-\frac{1}{2}\] done
clear
C)
\[n=3,\,l=1,\,{{m}_{l}}=-1,\,{{m}_{s}}=+\frac{1}{2}\] done
clear
D)
\[n=3,\,l=0,\,{{m}_{l}}=+1,\,{{m}_{s}}=-\frac{1}{2}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer144)
The radius of the first (lowest) orbit of the hydrogen atom is \[{{a}_{0}}.\] The radius of the second (next higher) orbit will be [MP PET 2002; MP PMT 2004]
A)
\[4{{a}_{0}}\] done
clear
B)
\[6{{a}_{0}}\] done
clear
C)
\[8{{a}_{0}}\] done
clear
D)
\[10{{a}_{0}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer145)
Which of the following transition will have highest emission wavelength [BHU 2003]
A)
\[n=2\text{ to} n=1\] done
clear
B)
\[n=1\text{ to }n=2\] done
clear
C)
\[n=2\text{ }\,\text{to}\,\,n=5\] done
clear
D)
\[n=5\text{ to }n=2\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer146)
When the wave of hydrogen atom comes from infinity into the first orbit then the value of wave number is [RPET 2003]
A)
109700 cm?1 done
clear
B)
1097cm?1 done
clear
C)
109 cm?1 done
clear
D)
None of these done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer147)
With the increase in principle quantum number, the energy difference between the two successive energy levels [RPET 2003]
A)
Increases done
clear
B)
Decreases done
clear
C)
Remains constant done
clear
D)
Sometimes increases and sometimes decreases done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer148)
In which of the following systems will the radius of the first orbit \[(n=1)\] be minimum [Kerala PET 2002; CBSE PMT 2003]
A)
Single ionized helium done
clear
B)
Deuterium atom done
clear
C)
Hydrogen atom done
clear
D)
Doubly ionized lithium done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer149)
If the binding energy of the electron in a hydrogen atom is 13.6 eV, the energy required to remove the electron from the first excited state of \[L{{i}^{++}}\] is [AIEEE 2003]
A)
122.4 eV done
clear
B)
30.6 eV done
clear
C)
13.6 eV done
clear
D)
3.4 eV done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer150)
Which of the following is quantised according to Bohr?s theory of hydrogen atom [MP PMT 2004]
A)
Linear momentum of electron done
clear
B)
Angular momentum of electron done
clear
C)
Linear velocity of electron done
clear
D)
Angular velocity of electron done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer151)
The shortest wavelength in the Lyman series of hydrogen spectrum is 912 Å corresponding to a photon energy of 13.6 eV. The shortest wavelength in the Balmer series is about [MP PMT 2004]
A)
3648 Å done
clear
B)
8208 Å done
clear
C)
1228 Å done
clear
D)
6566 Å done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer152)
Energy E of a hydrogen atom with principal quantum number n is given by \[E=\frac{-13.6}{{{n}^{2}}}eV\]. The energy of a photon ejected when the electron jumps from \[n=3\] state to \[n=2\] state of hydrogen is approximately [CBSE PMT 2004]
A)
1.5 eV done
clear
B)
0.85 eV done
clear
C)
3.4 eV done
clear
D)
1.9 eV done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer153)
The Bohr model of atoms [CBSE PMT 2004]
A)
Assumes that the angular momentum of electrons is quantized done
clear
B)
Uses Einstein?s photo-electric equation done
clear
C)
Predicts continuous emission spectra for atoms done
clear
D)
Predicts the same emission spectra for all types of atoms done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer154)
The colour of the second line of Balmer series is [J & K CET 2004]
A)
Blue done
clear
B)
Yellow done
clear
C)
Red done
clear
D)
Violet done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer155)
Which state of triply ionised Baryllium \[(B{{e}^{+++}})\] has the same orbital radius as that of the ground state of hydrogen [KCET 2004]
A)
n = 4 done
clear
B)
n = 3 done
clear
C)
n = 2 done
clear
D)
n = 1 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer156)
The ratio of areas within the electron orbits for the first excited state to the ground state for hydrogen atom is [BCECE 2004]
A)
16 : 1 done
clear
B)
18 : 1 done
clear
C)
4 : 1 done
clear
D)
2 : 1 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer157)
The kinetic energy of an electron revolving around a nucleus will be [BCECE 2004]
A)
Four times of P.E. done
clear
B)
Double of P.E. done
clear
C)
Equal to P.E. done
clear
D)
Half of its P.E. done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer158)
Taking Rydberg?s constant \[{{R}_{H}}=1.097\times {{10}^{7}}m\] first and second wavelength of Balmer series in hydrogen spectrum is [Pb. PMT 2004]
A)
2000 Å, 3000 Å done
clear
B)
1575 Å, 2960 Å done
clear
C)
6529 Å, 4280 Å done
clear
D)
6552 Å, 4863 Å done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer159)
The kinetic energy of electron in the first Bohr orbit of the hydrogen atom is [Pb. PET 2000]
A)
? 6.5 eV done
clear
B)
? 27.2 eV done
clear
C)
13.6 eV done
clear
D)
? 13.6 eV done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer160)
In the spectrum of hydrogen atom, the ratio of the longest wavelength in Lyman series to the longest wavelength in the Balmer series is [UPSEAT 2004]
A)
5/27 done
clear
B)
1/93 done
clear
C)
4/9 done
clear
D)
3/2 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer161)
In Bohr?s model of hydrogen atom, which of the following pairs of quantities are quantized [UPSEAT 2004]
A)
Energy and linear momentum done
clear
B)
Linear and angular momentum done
clear
C)
Energy and angular momentum done
clear
D)
None of the above done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer162)
The energy of the highest energy photon of Balmer series of hydrogen spectrum is close to [UPSEAT 2004]
A)
13.6 eV done
clear
B)
3.4 eV done
clear
C)
1.5 eV done
clear
D)
0.85 eV done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer163)
Energy of an electron in nth orbit of hydrogen atom is \[\left( k=\frac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}} \right)\] [DCE 2002]
A)
\[-\frac{2{{\pi }^{2}}{{k}^{2}}m{{e}^{4}}}{{{n}^{2}}{{h}^{2}}}\] done
clear
B)
\[-\frac{4{{\pi }^{2}}\,m\,k{{e}^{2}}}{{{n}^{2}}{{h}^{2}}}\] done
clear
C)
\[-\frac{{{n}^{2}}{{h}^{2}}}{2\pi \,k\,m{{e}^{4}}}\] done
clear
D)
\[-\frac{{{n}^{2}}{{h}^{2}}}{4{{\pi }^{2}}\,k\,m{{e}^{2}}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer164)
Which one of the relation is correct between time period and number of orbits while an electron is revolving in a orbit [DPMT 2003]
A)
\[{{n}^{2}}\] done
clear
B)
\[\frac{1}{{{n}^{2}}}\] done
clear
C)
\[{{n}^{3}}\] done
clear
D)
\[\frac{1}{n}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer165)
An electron changes its position from orbit \[n=4\] to the orbit \[n=2\] of an atom. The wavelength of the emitted radiation?s is (R = Rydberg?s constant) [BHU 2004]
A)
\[\frac{16}{R}\] done
clear
B)
\[\frac{16}{3R}\] done
clear
C)
\[\frac{16}{5R}\] done
clear
D)
\[\frac{16}{7R}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer166)
If the energy of a hydrogen atom in nth orbit is \[{{E}_{n}}\], then energy in the nth orbit of a singley ionized helium atom will be [BHU 2004]
A)
\[4{{E}_{n}}\] done
clear
B)
\[{{E}_{n}}/4\] done
clear
C)
\[2{{E}_{n}}\] done
clear
D)
\[{{E}_{n}}/2\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer167)
What is the ratio of wavelength of radiations emitted when an electron in hydrogen atom jump from fourth orbit to second orbit and from third orbit to second orbit [MH CET 2004]
A)
27 : 25 done
clear
B)
20 : 27 done
clear
C)
20 : 25 done
clear
D)
25 : 27 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer168)
The energy of electron in the nth orbit of hydrogen atom is expressed as \[{{E}_{n}}=\frac{-13.6}{{{n}^{2}}}eV\]. The shortest and longest wavelength of Lyman series will be [Pb. PET 2003]
A)
910 Å, 1213 Å done
clear
B)
5463 Å, 7858 Å done
clear
C)
1315 Å, 1530 Å done
clear
D)
None of these done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer169)
The ground state energy of hydrogen atom is ? 13.6 eV. What is the potential energy of the electron in this state [AIIMS 2005]
A)
0 eV done
clear
B)
? 27.2 eV done
clear
C)
1 eV done
clear
D)
2 eV done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer170)
The diagram shows-the energy levels for an electron in a certain atom. Which transition shown represents the emission of a photon with the most energy [AIEEE 2005]
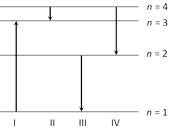
A)
I done
clear
B)
II done
clear
C)
III done
clear
D)
IV done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer171)
As the electron in Bohr orbit of Hydrogen atom passes from state \[n=2\] to \[n=1\], the kinetic energy K and potential energy U change as [MP PET 2005]
A)
K two-fold, U four-fold done
clear
B)
K four-fold, U two-fold done
clear
C)
K four-fold, U also four-fold done
clear
D)
K two-fold, U also two-fold done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer172)
The magnetic moment \[(\mu )\]of a revolving electron around the nucleus varies with principal quantum number n as [AIIMS 2005]
A)
\[\mu \propto n\] done
clear
B)
\[\mu \propto 1/n\] done
clear
C)
\[\mu \propto {{n}^{2}}\] done
clear
D)
\[\mu \propto 1/{{n}^{2}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer173)
Bohr's atom model assumes [KCET 2005]
A)
The nucleus is of infinite mass and is at rest done
clear
B)
Electrons in a quantized orbit will not radiate energy done
clear
C)
Mass of electron remains constant done
clear
D)
All the above conditions done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer174)
Radius of first Bohr orbit is r. What is the radius of 2nd Bohr orbit? [BHU 2005]
A)
8r done
clear
B)
2r done
clear
C)
4r done
clear
D)
\[2\sqrt{2r}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
